Dear readers, I am here with another exciting n’ informative article about ‘Hardware and Operative Systems’. In this post, we have revealed all those contents and common questions that click your mind while studying this topic, as mentioned below in the table of contents. Please read the article to get substantial knowledge about the topic. THANK YOU!
BASIC INFORMATION
Computer – Computer is an electronic device which accepts the data, processes it as per the given instructions and gives back the output.
Information – When the data is processed by the processing unit, i.e. CPU, it is known as Information.
Data – Data consists of set of characters, like alphabets, digits, or special characters that represent facts or figures.
Components – The computers are made up of many specific electronic parts known as components.
Hard disk – Hard disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device fixed inside a computer which is helpful in storing data and applications permanently.
Backup – Making a duplicate copy of data and information is called backup.
Port – A port is a connecting line or socket where other computers, wiring or peripheral devices (external devices) can be connected to transfer signals for different purposes.
Software – a set of instructions that instructs the computer what to do is called software.
Operating System (OS) – The OS is the system software that controls, manages and operates all the hardware and software components and devices, like- keyboard, mouse, tablet, headsets, smartphones, etc. The OS also looks after the language you are comfortable with, like- it removes the coding language so that you do not need to learn and understand tough signs and symbols.
INPUT & OUTPUT DEVICES
I/O or Input/Output is a major function of computers. One more phrase is on the way – PROCESS. So this becomes IPO or Input-Process-Output. So, now as we have collected a precise knowledge about IPO, let’s see what happens in this process and what all devices come across the way.
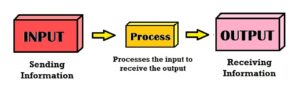
Input Devices
The devices through which the user sends information to the computer are called input devices. Some examples are – mouse, keyboard and digital camera.
Output Devices
The devices through which the user receives information from the computer are called output devices. Some examples are – monitor and printer.
Processing
When you enter or send some information to the computer through the input devices, for example: you write 5 + 5 on your keyboard, you receive an answer ‘10’. So, whatever you tell the computer to do, the computer processes and gives the output to the output devices, like monitor.
Read More Articles:
CPU (Processor)
Q. What do you understand by the term ‘CPU’?
CPU (Central Processing Unit) or the processor of the computer executes all the instructions given by a user or it runs a program or application, just like the brain of the computer. It processes each task we do on the computer, thus it is known as processor.
If you want to open a word document on your computer, you’ll give your instructions and they will go through cables connected to the CPU and once the CPU reads them, you are able to continue with your task.
Same goes with the human body. Analyze this case with yourself. If someone is pinching your hand, your body status will directly reach to the brain through veins and arteries, and once the brain gets to know you are in pain, you remove your hand.
Q. What are MHz and GHz?
MHz stands for Megahertz while GHz stands for Gigahertz, where ‘Hertz’ is the measuring unit to measure the processing speed. Mega means million while Giga means billion. So the more the MHz or GHz, the more the processing speed and faster the CPU can process instructions. For example, Windows 11 computer having a processing speed of 1.80 GHz.
PRIMARY MEMORY (Main Memory or RAM)
Q. What is RAM?
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the main memory which is used to store data and instructions temporarily. In simple words, when the processing of instructions is being done currently by the CPU. Once you save the data or instructions on the hard disk, it becomes permanent. Also, when you are in RAM, the data automatically gets erased when the computer is turned off.
(For example – when you open a word processor to create a document or you open Scratch to make an animation, the corresponding (resultant) instructions are loaded into RAM)
Q. What do you know about the MEMORY SIZE of a computer?
8 bits = 1 Byte
- 1024 Bytes = 1 Kilobyte (1 KB)
- 1024 KB = 1 Megabyte (1 MB)
- 1024 MB = 1 Gigabyte (1 GB)
- 1024 GB = 1 Terabyte (1 TB)
- 1024 TB = 1 Petabyte (1 PB)
- 1024 PB = 1 Exabyte (1 EB)
- 1024 EB = 1 Zettabyte (1 ZB)
- 1024 ZB = 1 Yottabyte (1 YB)
[KEY: 1024 is formed by writing 210]
Whatever we feed in the computer gets converted into a machine understandable code, called Machine Code. The computer understands only two states: ON (represented by 1) and OFF (represented by 0). These two digits – 0 and 1 are called Binary digits or Bits. The data is stored in the computer memory in the form of bits and is measured in Bytes.
SECONDARY MEMORY (Hard Disk & Removable Storage)
Q. What is SECONDARY MEMORY?
Secondary memory is a permanent memory in which the data and information is stored eternally until and unless the information is explicitly deleted. Also, whatever data the secondary memory consist, does not get erased even if your computer is being switched off.
Q. What are REMOVABLE STORAGE DEVICES?
The devices that are portable and can hold the data and information as a kind of backup of the original data are known as removable storage devices. They can also be used as a data sharing agent by which the backup data contained in it can be connected to another device and the data can be transferred. HDD (Hard Disk Drives), ROM (Read-only Memory: permanent storage), Flash/Pen drives; CD/DVD, magnetic tapes and SD card are few examples of removable storage devices.
The purpose to backup data and information can also be seen online when you send a copy of the data to yourself (another ID) through Gmail. You can even copy it on the Google Drive which is a universal means of storage and can be accessed from anywhere in the world once you have internet connection and a Gmail account.
POWER SUPPLY
Definition: A power supply is a big box like battery which supplies power to all components of the computer. The power is sent to the motherboard and other components through many varieties of cables connected to the components.
Power supply unit converts power from the wall outlet=110 volts (usually AC – Alternating Current) to the type of power required by the computer (usually DC – Direct Current).
The power button (to switch on or off) in computers is generally seen on the front panel of the CPU, while in laptops it is commonly available above the keyboard.
MONITOR (Display)
Definition
The monitor is an output device that consists of a visual display screen through which the main information and data can be viewed and all tasks can be performed.
The monitor is externally connected to the VGA port (a component on motherboard used to connect a monitor or a LCD). There are different variety of monitors varying there shapes and sizes and quality of display. This is because of different revolutions of different monitors. Resolution is defined as the number of dots on a monitor called ‘pixels’ which is the only means to increase or decrease the revolution of the monitor.

The more the number of pixels, the sharper and brighter the display will appear. For example – You have two visual displays; both are having same resolution but different sizes. In this case, the larger display will have its pixels spread all over the screen and thus will make the screen blurred and less sharp. Whereas, the smaller screen has its pixels spread over a short distance and accumulate over a small area, thus resulting in sharper and brighter result. Therefore, this means that the sharpness of a display depends upon the size and resolution of a monitor.
The size of a display depends on two factors:
1) Aspect ratio: width to height 2) Screen size: diagonal length
The pixels appear in the horizontal and vertical dimensions. For example, a display having a resolution of 1280×700 pixels means that 1280 pixels are present on the X axis (horizontal) while 700 pixels are present along the Y axis (vertical).
When a huge display has to be there on a public place to convey some information or medical imaging, large size monitors are required as of 40 inches along will high resolution. These are generally expensive.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is nowadays, the trendy technology to represent monitors, as LCDs provide a better display sharpness and brightness as compared to the previous technology. These days, {15, 17, 19 and 21} inches are most popular sizes used for the same.
BIOS Software and Booting
Q. How does a computer start?
A computer requires some software to get switched on. Therefore, a software called Basic Input/Output System (BIOS), operating system and application software are required.
First of all, when you click the power button of a computer, the BIOS software starts and boots the computer. BIOS software is located on a small chip of ROM (flash memory) present on the motherboard.
Therefore, BIOS is the first software which runs on the computer when it is turned on.
Q. What is the function of BIOS?
The most significant role of BIOS is to load the operating system into memory.
Another function of BIOS is to check whether all hardware components (keyboard, mouse, CD/DVD, display card, hard disk) are working or not before starting a computer. While the computer starts, messages pop-up on the starting screen regarding the status of the hardware. In case any of the hardware components are malfunctioning, then the BIOS software automatically gets us to an error message.
BIOS software is also an instructor as it instructs the CPU where to locate the operating system on the hard disk.
Q. What is BOOTING?
The process by which BIOS gives control of the computer to the operating system is called booting.
OPERATING SYSTEM (OS)
As it is already mentioned at the top of my article, (BASIC INFORMATION column), you can see that how you can define the OS. For your convenience, you can view it below as well:
Operating System (OS) – The OS is the system software that controls, manages and operates all the hardware (peripherals) and software (applications) components. The OS also looks after the language you are comfortable with, like- it removes the coding language so that you do not need to learn and understand tough signs and symbols. Some common examples of operating systems available to users’ are (Windows, Linux and MAC); and their further versions.
The OS finds its place on the hard disk {secondary memory – (read the table of contents)}.
BIOS and OS have a big difference for one parameter, i.e. BIOS only helps in checking all hardware components and loading into OS along with very limited instructions. Once BIOS has loaded the OS, all work is transferred to OS. From there, getting login, executing applications, do processing, input, output and all other functions are performed under OS. The usage of computer begins when the OS wakes up.
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
Definition: A software that is written in specific programming languages is called an application software. It is designed by programmers for specific categories, like- games; word processing; paint; editing software or animation; email; etc. Some applications are as follows- Scratch, Sticky Notes and Filmora–Video Editor.

A coding software is itself an application, like- Visual Studio Codes and BASIC-256.

These applications can be downloaded or deleted anytime and anywhere. They are stored in the hard disk as a permanent storage until it is explicitly deleted.
Dear readers, we hope that this article is very useful and fruitful to you. If you further have any queries, you can drop in the comment section. You may write your valuable feedback for the article prepared. THANK YOU!!

