History of Computers | KnockLedge
Major Milestones | People Responsible for the development
Hello Friends,
In this post of history of computers | KnockLedge we get to know that the history of computers has been immense. As new ideas of new people are presented, new technologies are approaching the whole world. This way, we are growing each day using trouble-free technology.
The prior centuries were using simple gadgets which involved machinery as big as a hall, and were designed to perform simple calculations; like addition and subtraction. As new generations are arriving, computers are also able to see their new complex and advanced generations.
Till date, the evolution of computers has become so powerful that the 19th century and the latest technology are both comparatively unidentifiable. Such as the Analytical Engine by Charles Babbage and MacBook Computers by Apple Company are both very different from every parameter.
It’s time for us to get a universal view of the topic. In this article, we are going to dive into the pre-historic computers and devices along with their inventors and usage.
ABACUS | HISTORY OF COMPUTERS
Abacus was the first computer in the history. It was first invented by Babylonia (Mesopotamia) in around 2400 B.C. and first used by China in around 500 B.C. Its main purpose was to perform basic arithmetic operations. It is known as the first calculation device in the world.

NAPIER’S BONES
The Napier’s Bones was invented in 1614 by John Napier in Scotland. It was a manual device composed of bone or ivory strips which was designed to perform multiplication, division and calculation of square and cube roots. This device was the first to comprise of decimal points.

SLIDE RULE
Slide Rule was a manual device which was invented in 1622 by William Oughtred. It was a mechanical analogue computer consisting of a ruler with a movable section in the middle which was intended to perform multiplication, division, exponents, roots, logarithm and trigonometry. But, addition and subtraction cannot be performed using this device which is surely, a limitation of this device.
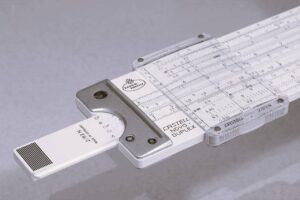
PASCALINE | Pascal Calculator
Pascaline was invented in 1642 by Blaise Pascal in France. He built this mechanism to facilitate his father, a tax accountant. It was a simple device or a calculator that was used to perform addition and subtraction, thus overcoming the limitation of slide rule, but overall it was very expensive.
Working of PASCALINE
Pascaline was basically a wooden machine which consisted of many wheels or gears side-by-side. Once you move one gear completely, the neighboring gear will automatically start rotating. Several small windows sort of screens will also appear above the wheels which show us the output/total.
STEPPED RECKONER | Leibnitz Wheel
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz invented the Stepped Reckoner, also known as Leibnitz Wheel, in 1673 in Germany. This device was basically an upgraded version of Pascaline. So in this digital calculation machine, we can make the use of all the four mathematical operators, i.e. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. The derivation of its name is from the translation of German word ‘Staffelwalze’, which means Stepped drum.
ARITHMOMETER
Arithmometer was the first commercially successful mechanical calculator invented in 1820 by Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar in France. Thomas wanted to aid himself for the French Army which required numerous calculations. Using this device, the user can easily perform four basic mathematical operators, i.e. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Additionally, Arithmometer was produced in a large amount (high production), therefore having more publicity.
DIFFERENCE ENGINE
Difference Engine was a mechanical calculating computer invented in 1822 by Charles Babbage, popularly known as the ‘Father of Modern Computer’. He has created such an automatic machine that the user can tabulate table of mathematics and statistics (simple calculations).

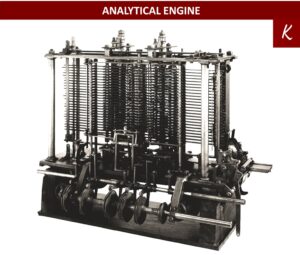
ANALYTICAL ENGINE
Charles Babbage designed The Analytical Engine in 1833, as a general-purpose computer. It was an automatic and mechanical calculator competent of working out any mathematical question also having a memory to store information. To use this device, the user had to use punched cards.
SCHEUTZIAN CALCULATION ENGINE
Per Georg Scheutz developed Scheutzian Calculation Engine in 1843. This machine was almost based on the Difference Engine by Charles Babbage. In this mechanism, the user can work out mathematical problems along with printing those solutions. Consequently, it became the first printing calculator. The user can work out multiplication, division and exponents using this machine.
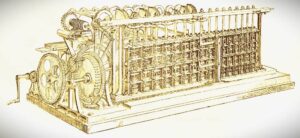
TABULATING MACHINE
Herman Hollerith first time invented the Tabulating Machine in 1890. This machine was so useful that later, it gave rise to ‘Hollerith’s Tabulating Machine Company’. After sometime (1924), this company was transformed to IBM (International Business Machine). It was an electromechanical machine in which Hollerith made the use of punched cards as an input. The main purpose of this device was to recapitulate (sum-up) information and bookkeeping.
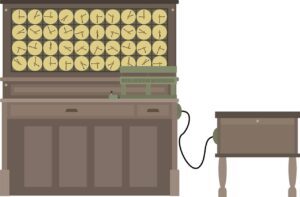
HAVARD MARK 1
Mark 1 was the first programmable computer. Howard H. Aiken invented it in 1943. This computer was a general purpose electromechanical computer. Its other name is IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC). Like the tabulating machine, this computer is also based on punched cards. The main purpose of Mark 1 is to work out large and complex mathematical problems easily. It can consist of the four mathematical operators and all previous topics. Mark 1 was a massive computer that was approximately 8 feet high, 50 feet long and was about 5 tons of weight.

Z1 COMPUTER
The Z1 computer was the first freely programmable mechanical computer. Konrad Zuse, a German civil engineer, invented it in 1936-1938. According to the scenario of Germany, people consider Zuse as the father of computer. It was a motor driven computer on the concept of binary floating-point numbers and could execute the four basic mathematical operators.

ABC | Atanasoff-Berry Computer
Atanasoff-Berry Computer or ABC was the first automatic electronic digital computer, whose invention took place in 1939-1942 at Lowa State University. The derivation of the name of this mechanism is after the name of two inventors – Professor John Vincent Atanasoff & Clifford Berry. With the help of one of his student (Clifford Berry), he completed his spectacular thinking by the conception of ABC.
Function: ABC could easily support problems related to physics and linear equation.

ENIAC | Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) was first programmable general-purpose electronic digital computer. John W. Mauchly and John Presper Eckert in 1945 invented this computer. ENIAC weighed 30 tons, occupying 1800 square feet space. USA developed it during the World War II which had major use to calculate artillery firing tables (military need).

Read More…
• File Management | Organization of Data
5 COMPUTER GENERATIONS
As each new generation is imminent, new technologies with more processing speed, memory and power are approaching the world. Day by day, we are getting better technology which we can use for our betterment. Here, I present some information about the five computer generations till date.
FIRST GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (1942-1954)
The first generation of computers used vacuum tube technology. These vacuum tubes produced immense heat, therefore they were very expensive. They produced so much heat that the requirement of A.C.s were at a huge. Only large organizations could afford such gigantic computers. These computers were neither reliable nor portable. Users could only use machine language (binary codes: 0 and 1).. First generation had slow input/output devices and they consumed a lot of electricity.
ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701 and IBM-650 were some popular computers of this generation.
SECOND GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (1952-1964)
The second generation of computers used transistor technology. These transistors were compact, consumed less electricity, produced less heat, cheaper and more reliable and faster as compared to vacuum tubes. Despite of having so many updated features, still the prices were very high. The requirement of A.C.s was still a big factor. These computers supported machine language and assembly language. Programming languages like FORTRAN and COBOL were available in this generation. Users could only use machine language (binary codes: 0 and 1). First generation had slow input/output devices and they consumed a lot of electricity.
IBM-1620, IBM-7094, CDC-1604, CDC-3600 and UNIVAC-1108 were some advanced computers of this generation.
THIRD GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (1964-1972)
The second generation of computers used Integrated Circuits (IC). One IC consisted of numerous transistors, capacitors and resistors. These IC’s had small size, were more reliable, generated very less heat, were more faster, had less maintenance and consumed very less electricity, as compared to transistors. Regardless of having so many competent features, still it was very costly. The requirement of A.C.s was still a big issue. Real-time, remote processing, time-sharing, along with multi-programming operating system were handy. These computers had an integration of high level languages, like: COBOL, PASCAL, BASIC, ALGOL-68 and FORTRAN II-IV.
IBM-360, IBM-370, IBM-168, TDC-316, Honeywell-6000 and PDP (Personal Data Processor) were some classy computers of this generation.
FOURTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (1972-1990)
The second generation of computers used Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) Circuits. A single chip of VLSI circuits has 5000 transistors. We say that the fourth generation of computers has come up with microcomputers. This generation invented simple, portable, reliable, miniature and cheap mechanism. These computers were affordable (not expensive). To cool down the inventions, there was no requirement of air conditioner. Networks and Distributed Operating System were the new features. Personal computers (PCs) were introduced with the Internet technology. Hence, network became very popular as well as very obliging. These computers were efficient and understandable as high level languages were into play, like: C, C++, DBASE, Python, Ruby, SQL, Perl and PHP.
STAR-1000, DEC-10, PDP-11, CRAY-1 and CRAY-X-MP (supercomputer) were some trendy computers of this generation.
FIFTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (1990-till date)
The second generation of computers used Ultra Large Scale Integrated (ULSI) technology. We say that the fourth generation of computers has come up with microprocessor chips having more than ten million electronic components. Today’s generation is completely based on high-tech technology of parallel processing hardware and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Artificial Intelligence software is emerging as a branch so as to construct mechanism that thinks and acts like humans. AI is nowadays becoming immense. Technology finally upgrades Games, Robotics, Facts, Videos, Social Media and answers to every question. Using Internet, search engines, Google maps, YouTube videos etc. are running. These computers are affordable, compact in size, with user-friendly display and powerful processing speed. These computers support all handy and human understandable languages, like: Prolog, OPS5 and Mercury.
Notebook, Desktop, Laptop and Ultrabook are some chic computers of today’s generation.
MILESTONES: Modern Day Computers & Internet
1. Macintosh 128K (in 1984)

2. Windows Launched by MICROSOFT (in 1985)

3. World Wide Web (www) [in 1989]
![World Wide Web (www) [in 1989]](http://theknockledge.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Webp.net-compress-image-18-300x212.jpg)
4. Google Launched (in 1998)

5. Broadband (in the 2000s)

6. YouTube was launched (in 2005)

7. iPhone Launched by Apple (in 2007)

8. Amazon Got Launched – Jeff Bezos

IMPORTANT PEOPLE: Responsible for Development
1. Charles Babbage, father of computer
2. Douglas Engelbart, inventor of MOUSE
3. Tim Berners Lee, inventor of WORLD WIDE WEB
4. Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla Motors & SpaceX
5. Larry Page, Co-founder of Google
6. Bill Gates, Co-founder of Microsoft
7. Mark Zuckerberg, Chief Executive Officer of Facebook
8. Jeff Bezos, Executive Chairman of Amazon
9. Warren Buffett, CEO of Berkshire Hathaway
10. Larry Ellison, American business magnate

